Bachelor of commerce or B.com is a widespread course among commerce students. Today in this article we will discuss- “What to do after B.com?”.
According to NEP (New education policy), there will be a total of 6 semesters in a 3-year duration- 2 semesters every year.
Typically this course is of 3-year duration which may Involve “New education policy prescribed” subjects like:
- Business Organisation
- Business communication
- Business Statistics
- Company Law
- Cost accounting
- Financial Accounting
- Computerized accounting, and many more.
According to the “New education policy 2020”, there may be 29 subjects for all 6 semesters of the B.com course. So we can say that B.com is a Business and accounting-oriented educational course.
What to do after B.com?
- Degree Courses
- MBA
- PGDM
- M.com
- MCA
- LLB
- B.Ed
- Professional certificate courses
- CA
- CS
- ACCA
- CMA
- CFA
- CFP
- Skill Development Courses
- Data Science
- Business Analytics
- Stock market
- programming
- Web design/ App development
- VFX and Animation
- Digital Marketing
- Ethical Hacking
- Personality development courses
- Government Jobs
- SSC CGL
- IBPS PO
- RRB
- CSAT
- Special recruitment areas
- Accounting and Auditing
- Tax advisory service
- Financial service
- commercial banking
- International banking
- Insurance service
- Telecommunication service and BPO’s
- Manufacturing service
- Government service
- Policy Planning
- Educational Institute
- Informational technology
- Special Job titles for B.com graduate
- Chartered Accountant (CA)
- Marketing Management
- Investment Banker
- Human resource manager
- Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
- Chartered Public Accountant (CPA)
- Actuary
- Cost accountant
- Business Accountant and taxation
- Retail manager
- Company Secretary
- Personal Financial Advisor
- Research Analyst
- Chief Executive Officer (CFO)
- Entrepreneur

The best part of a commerce subject is that it provides you with a wide area of fields and scope. and so our B.comcourse also provides us the lots of- jobs, degree courses, certificates, etc.
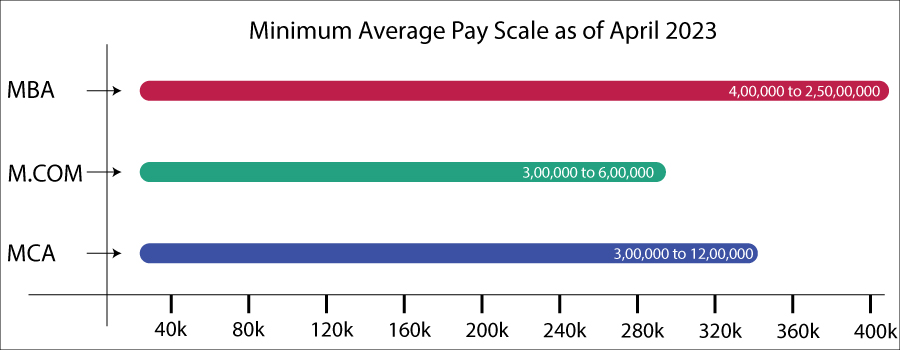
Salary comparison of M.com, MBA, and MCA
M.com, MBA, and MCA are the famous streams for a B.com degree holder.
Salaries for individuals with an M.Com, MBA, or MCA degree can vary depending on several factors such as their experience, industry, location, and company.
In general, MBA graduates tend to have the highest salaries among these three degrees, followed by MCA and then M.Com. However, this can also depend on the specialization and focus of the degree.
Here are some approximate salary ranges based on data from PayScale as of March 2023:
- M.Com: The average salary for an M.Com graduate in India is around INR 300,000 to INR 600,000 per annum. However, this can vary widely depending on the industry and experience.
- MBA: The average salary for an MBA graduate in India can range from INR 400,000 to INR 2,500,000 per annum. MBA graduates with a specialization in fields such as finance, marketing, and operations tend to earn higher salaries.
- MCA: The average salary for an MCA graduate in India can range from INR 300,000 to INR 1,200,000 per annum. MCA graduates with experience in software development and programming tend to earn higher salaries.
Degree Courses
MBA (Master of Business Administration)
MBA stands for Master of Business Administration. It is a graduate degree program designed to provide students with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the business world. MBA programs typically cover a range of business topics, including accounting, finance, marketing, operations, and management.
The MBA degree is highly regarded in the business world and is often seen as a pathway to top-level management positions in a variety of industries. Many MBA programs also offer opportunities for students to network with other professionals and gain hands-on experience through internships and other experiential learning opportunities.
PGDM (Post graduate diploma in management)
PGDM stands for Post Graduate Diploma in Management. It is a postgraduate diploma program in management that is offered by many institutes in India. The program is similar to an MBA in terms of the curriculum and the skills and knowledge it provides to students. However, PGDM programs are typically more focused on practical skills and industry-specific knowledge.
Unlike an MBA, which is offered by universities, PGDM programs are offered by autonomous institutes that are approved by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE). PGDM programs are designed to be more flexible and responsive to changes in industry trends and demands. They often have more industry exposure and hands-on training components, and the curriculum is updated regularly to keep up with the latest business practices.
Overall, PGDM programs are a good option for students who want a more practical and industry-focused management education, while MBA programs are a better choice for those who want a more traditional and academic management education.
M.com (Master of Commerce)
MCom stands for Master of Commerce. It is a postgraduate degree program in commerce that is designed to provide students with advanced knowledge and skills in various areas of commerce such as accounting, finance, economics, marketing, and management.
The MCom program is usually two years long and is offered by universities and colleges around the world. It is a continuation of undergraduate studies in commerce or related fields and is aimed at providing students with a deeper understanding of various aspects of commerce.
The curriculum of the MCom program includes advanced courses in areas such as financial accounting, corporate finance, taxation, auditing, and business law. It also provides students with opportunities to specialize in specific areas of commerce such as international business, human resource management, and marketing.
Upon completion of the MCom program, graduates can pursue careers in various fields such as finance, accounting, banking, consulting, and business management. They can also opt for further education such as a Ph.D. in commerce or related fields.
MCA (Master of computer application)
MCA stands for Master of Computer Applications. It is a postgraduate degree program in computer science that is designed to provide students with advanced knowledge and skills in various areas of computer science such as software development, programming, database management, and web design.
The MCA program is typically three years long and is offered by universities and colleges around the world. It is a continuation of undergraduate studies in computer science or related fields and is aimed at providing students with a deeper understanding of various aspects of computer science.
The curriculum of the MCA program includes advanced courses in areas such as programming languages, data structures, algorithms, computer networks, software engineering, and database management. It also provides students with opportunities to specialize in specific areas of computer science such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and mobile application development.
Upon completion of the MCA program, graduates can pursue careers in various fields such as software development, database administration, web development, network administration, and cybersecurity. They can also opt for further education such as a Ph.D. in computer science or related fields.
LLB (Bachelor of law)
LLB stands for Bachelor of Laws. It is an undergraduate degree program in law that is designed to provide students with a foundational understanding of legal principles and concepts.
The LLB program typically takes three to five years to complete, depending on the country and the educational institution offering the program. The curriculum of the LLB program includes courses in various areas of law such as criminal law, civil law, constitutional law, administrative law, and commercial law. It also covers legal research and writing, legal theory, and ethics.
Upon completion of the LLB program, graduates can pursue a career in various fields such as law practice, corporate law, legal research, public service, and academia. In most countries, however, in order to practice law as a licensed lawyer, LLB graduates must pass a bar exam and meet other requirements mandated by the respective jurisdiction’s regulatory body for legal practice.
Overall, the LLB program is an excellent option for students who want to pursue a career in law and make a positive impact on society by advocating for justice and equality under the law.
B.Ed (Bachelor of education)
B.Ed stands for Bachelor of Education. It is an undergraduate degree program that is designed to prepare students for a career in teaching.
The B.Ed program typically takes two years to complete and is offered by universities and colleges around the world. The curriculum of the B.Ed program includes courses in various areas such as educational psychology, educational technology, curriculum development, teaching methodology, and classroom management.
The program also provides students with opportunities for practical training through supervised teaching practice in schools. This allows students to gain hands-on experience in teaching and develop their teaching skills and competencies.
Upon completion of the B.Ed program, graduates can pursue a career as a teacher in primary, secondary, or higher education. They can also opt for further education such as a master’s degree in education or related fields.
Overall, the B.Ed program is an excellent option for students who are passionate about teaching and want to make a positive impact on the lives of their students by providing them with quality education and facilitating their intellectual and personal growth.
Professional certificate courses
CA (chartered accountant)
CA stands for Chartered Accountant. It is a professional designation conferred upon individuals who have completed the Chartered Accountancy course and have met the requirements set by the regulatory body responsible for the regulation of the profession in the respective country.
The Chartered Accountancy course typically takes three to five years to complete and consists of theoretical education, practical training, and passing a series of examinations. The curriculum of the course includes various areas of accounting such as financial accounting, cost accounting, taxation, auditing, and corporate finance.
Chartered Accountants are trained to provide a wide range of financial services such as auditing, accounting, taxation, financial reporting, and consulting services to businesses and individuals. They play a critical role in ensuring the financial health and stability of organizations and are held in high regard for their expertise and professionalism.
Upon completion of the Chartered Accountancy course and meeting the regulatory requirements, individuals can apply for a license to practice as a Chartered Accountant. Chartered Accountants can work in various fields such as public accounting, industry, government, and academia. They can also pursue further education such as a master’s degree in accounting or related fields to enhance their knowledge and skills.
CS (computer science)
A Computer Science certificate is a type of academic or professional certification that demonstrates proficiency and knowledge in computer science. It is usually obtained after completing a program of study, either online or at a college or university, that covers topics such as programming, algorithms, data structures, database systems, software development, and computer systems.
Some computer science certificates are intended for those with a bachelor’s or master’s degree in another field who want to gain additional computer science knowledge and skills, while others are designed for those without a computer science background who want to learn the basics of programming and software development.
Additionally, some computer science certificates are geared towards specific areas of computer science, such as cybersecurity or artificial intelligence, while others provide a more general overview of the field.
ACCA (Association of chartered certified accountants)
ACCA stands for the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants. It is a globally recognized professional accounting qualification that provides a broad knowledge of accounting, finance, and business management.
The ACCA certificate is awarded to those who have completed the required exams, practical experience, and ethics module as outlined by the ACCA. It is a highly respected qualification that demonstrates the holder’s technical expertise, ethical standards, and professional competence in the field of accounting and finance.
ACCA certification is recognized by employers and regulatory bodies worldwide and can open up many career opportunities in various industries and sectors.
CMA (certified management accountant)
CMA stands for Certified Management Accountant, which is a professional certification in management accounting and financial management. The CMA certification is offered by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) in the United States.
The CMA certificate signifies that the holder has achieved a high level of professional competence in the fields of management accounting and financial management. The certification program covers topics such as financial planning, analysis, control, and decision support, as well as professional ethics and corporate governance.
To earn the CMA certification, candidates must meet educational and experience requirements, pass a two-part exam, and adhere to a code of ethics. The CMA certification is globally recognized, and holders of the certificate are in high demand in various industries and sectors, including finance, accounting, consulting, and manufacturing.
CFA (chartered financial analyst)
CFA stands for Chartered Financial Analyst, which is a professional designation offered by the CFA Institute. The CFA designation is considered to be one of the most respected and recognized certifications in the field of finance and investment management.
The CFA program covers topics such as financial analysis, portfolio management, ethics, and professional standards. To earn the CFA designation, candidates must pass three levels of exams, meet educational and professional requirements, and have relevant work experience.
The CFA designation is globally recognized, and holders of the certificate are highly respected and sought after in the finance industry. CFA charter holders work in a wide range of positions, including investment management, financial analysis, research, consulting, and risk management.
CFP (certified financial planner )
CFA stands for Chartered Financial Analyst, which is a professional designation offered by the CFA Institute. The CFA designation is considered to be one of the most respected and recognized certifications in the field of finance and investment management.
The CFA program covers topics such as financial analysis, portfolio management, ethics, and professional standards. To earn the CFA designation, candidates must pass three levels of exams, meet educational and professional requirements, and have relevant work experience.
The CFA designation is globally recognized, and holders of the certificate are highly respected and sought after in the finance industry. CFA charter holders work in a wide range of positions, including investment management, financial analysis, research, consulting, and risk management.
Skill Development Courses
Data Science
A data science course is a program that teaches individuals the skills and knowledge needed to work with data, extract insights, and make informed decisions. Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistics, mathematics, programming, and domain expertise to analyze and interpret complex data.
A typical data science course covers topics such as data analysis, machine learning, statistical modeling, data visualization, data management, and communication. It may also include courses on specific tools and technologies used in data science, such as Python, R, SQL, Hadoop, and Spark.
Data science courses are designed to help individuals develop the skills needed to work with big data and extract insights from it. These courses are in high demand as more and more organizations are looking to leverage their data to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge. Data science courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Business Analytics
A business analytics course is a program that teaches individuals how to use data and analytical methods to make data-driven business decisions. Business analytics is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistics, mathematics, programming, and business acumen to analyze and interpret complex data.
A typical business analytics course covers topics such as data analysis, statistical modeling, data visualization, data management, and communication. It may also include courses on specific tools and technologies used in business analytics, such as Excel, SQL, and Tableau.
The goal of a business analytics course is to help individuals develop the skills needed to work with data and use it to solve business problems. These courses are in high demand as more and more organizations are looking to leverage their data to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge. Business analytics courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Stock Market
A stock market course is a program that teaches individuals about investing in the stock market. The stock market is a marketplace where publicly traded companies issue shares of their stock to raise capital. These shares are bought and sold by investors, and the price of the shares fluctuates based on supply and demand.
A typical stock market course covers topics such as stock valuation, financial statement analysis, market analysis, portfolio management, and risk management. It may also include courses on specific investment strategies, such as value investing, growth investing, and dividend investing.
The goal of a stock market course is to help individuals develop the skills needed to invest in the stock market and make informed investment decisions. These courses are in high demand as more and more individuals are looking to invest their money and grow their wealth. Stock market courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Programming
A programming course is a program that teaches individuals how to write code and develop software applications. Programming is the process of writing instructions that a computer can understand and execute, using programming languages such as Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript.
A typical programming course covers topics such as programming fundamentals, data structures and algorithms, object-oriented programming, web development, and mobile app development. It may also include courses on specific programming languages and tools, such as SQL, HTML, CSS, and Git.
The goal of a programming course is to help individuals develop the skills needed to write code and develop software applications. These courses are in high demand as more and more organizations are looking to hire software developers and programmers to build their products and services. Programming courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Web design/ App development
Web design and app development are two related fields that involve creating digital products such as websites, web applications, and mobile applications.
Web design refers to the process of creating the visual and functional aspects of websites, such as the layout, color scheme, and user interface. Web designers use various tools and technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create engaging and user-friendly websites.
App development, on the other hand, refers to the process of creating software applications for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. App developers use various programming languages such as Java, Swift, and Kotlin to build applications that run on different mobile operating systems such as iOS and Android.
Both web design and app development require a combination of technical and creative skills, including knowledge of programming languages, design principles, user experience, and project management. Web designers and app developers work together to create digital products that meet the needs of their clients and users.
VFX and Animation
Anyone from any field can try their hands at VFX and Animations.
VFX (Visual Effects) and animation are two related fields that involve creating visual content for various media such as films, TV shows, video games, and advertising.
VFX refers to the process of creating or manipulating digital imagery using computer-generated imagery (CGI) techniques. VFX artists use various software tools such as Adobe After Effects, Autodesk Maya, and Cinema 4D to create visual effects such as explosions, fire, and special powers. VFX is used to enhance or create visual elements that cannot be captured on camera, such as monsters, spaceships, and magical environments.
Animation, on the other hand, refers to the process of creating the illusion of motion and bringing characters and environments to life using various techniques such as traditional hand-drawn animation, 3D computer animation, and stop-motion animation. Animators use software tools such as Adobe Animate, Toon Boom Harmony, and Autodesk Maya to create animations for various media such as TV shows, movies, and video games.
Both VFX and animation require a combination of technical and artistic skills, including knowledge of software tools, storytelling, character design, and motion graphics. VFX artists and animators work together to create engaging and immersive visual content for their clients and audiences.
Digital Marketing
A digital marketing course is a program that teaches individuals how to use digital channels to promote products, services, or brands. Digital marketing is a rapidly evolving field that includes a range of techniques and strategies, such as search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, email marketing, content marketing, and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising.
A typical digital marketing course covers topics such as digital marketing fundamentals, website optimization, social media marketing, email marketing, content marketing, digital advertising, analytics, and strategy. It may also include courses on specific tools and platforms used in digital marketing, such as Google Analytics, Facebook Ads, and HubSpot.
The goal of a digital marketing course is to help individuals develop the skills needed to create and implement effective digital marketing campaigns. These courses are in high demand as more and more organizations are looking to leverage digital channels to reach their target audiences and achieve their marketing goals. Digital marketing courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Ethical Hacking
An ethical hacking course is a program that teaches individuals how to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks with the goal of improving their security. Ethical hacking, also known as “white hat” hacking, is the practice of using hacking techniques for the purpose of identifying and fixing security weaknesses, rather than causing harm or stealing data.
A typical ethical hacking course covers topics such as network and system security, penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, web application security, and social engineering. It may also include courses on specific tools and techniques used in ethical hacking, such as Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark.
The goal of an ethical hacking course is to help individuals develop the skills needed to assess the security of computer systems and networks and identify potential security threats. These courses are in high demand as organizations are looking for ways to protect their systems and data from cyber-attacks. Ethical hacking courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Personality development courses
A personality development course is a program that helps individuals to develop and improve their personal and interpersonal skills, confidence, and overall personality. The course aims to help individuals to become more self-aware and to identify areas for personal growth and improvement.
A typical personality development course covers topics such as communication skills, interpersonal skills, time management, leadership skills, goal setting, self-confidence, and emotional intelligence. It may also include courses on specific areas of personal development, such as public speaking, assertiveness, stress management, and personal branding.
The goal of a personality development course is to help individuals to develop the skills and qualities needed to succeed in their personal and professional lives. These courses are in high demand by individuals looking to enhance their career prospects, build better relationships, and improve their overall quality of life. Personality development courses are available both online and in traditional classroom settings, and they are offered by many universities, colleges, and online learning platforms.
Government Jobs
SSC CGL
SSC CGL stands for Staff Selection Commission Combined Graduate Level Examination. It is a national-level examination conducted by the Staff Selection Commission (SSC) for the recruitment of various Group B and Group C posts in various government departments and ministries.
The SSC CGL exam is conducted in four stages, namely Tier I, Tier II, Tier III, and Tier IV. The Tier I exam is a computer-based test consisting of objective-type questions in subjects such as general intelligence and reasoning, general awareness, quantitative aptitude, and English language. The Tier II exam is also a computer-based test consisting of multiple-choice questions in subjects such as Quantitative Abilities, English Language and Comprehension, Statistics, and General Studies (Finance and Economics).
The Tier III exam is a descriptive test that tests the writing skills of the candidates, while the Tier IV exam is a skill test that evaluates the proficiency of the candidates in computer skills, data entry, and analysis.
SSC CGL is one of the most sought-after exams in India, and lakhs of candidates appear for it every year. The exam provides a great opportunity for candidates to get a job in various government departments and ministries at a Group B or Group C level.
IBPS PO
IBPS PO stands for Institute of Banking Personnel Selection Probationary Officer. It is a national-level examination conducted by the Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) for the recruitment of Probationary Officers (PO) in various public sector banks in India.
The IBPS PO exam is conducted in three stages, namely Preliminary Examination, Main Examination, and Interview. The Preliminary Examination is a computer-based test consisting of objective-type questions in subjects such as English Language, Quantitative Aptitude, and Reasoning Ability. The Main Examination is also a computer-based test consisting of multiple-choice questions in subjects such as Reasoning and Computer Aptitude, General/Economy/Banking Awareness, English Language, and Data Analysis and Interpretation.
Candidates who qualify for the Main Examination are then called for an Interview, which is the final stage of the selection process. The IBPS PO exam is highly competitive, and candidates need to prepare well in advance to clear the various stages of the exam.
The exam provides a great opportunity for candidates who are interested in a career in banking to get a job in various public sector banks in India.
RRB
RRB stands for Railway Recruitment Board. It is a government organization that conducts recruitment exams to fill various vacancies in the Indian Railways.
There are 21 RRBs in India, and they are responsible for conducting recruitment exams for different regions and zones of the Indian Railways. The exams conducted by the RRBs include various posts such as Junior Engineer, Assistant Loco Pilot, Technician, Group D, and others.
The selection process for RRB exams varies based on the post and the level of the exam. Generally, the selection process involves a computer-based test, physical efficiency test, medical examination, and document verification.
Candidates who clear the various stages of the selection process are offered a job in the Indian Railways. A job in the Indian Railways is considered to be a highly coveted one as it offers job security, a good salary, and various other benefits.
CSAT
CSAT stands for Civil Services Aptitude Test. It is a part of the Civil Services Examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) in India. The CSAT was introduced in 2011 as a replacement for the earlier Preliminary Examination.
The CSAT is conducted in two stages, namely the Preliminary Examination and the Main Examination. The Preliminary Examination consists of two papers: General Studies and Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT). The General Studies paper tests candidates’ knowledge in various subjects such as History, Geography, Economy, Polity, and Current Affairs. The CSAT paper tests the candidates’ aptitude in areas such as Logical Reasoning, Analytical Ability, and Comprehension.
Candidates who clear the Preliminary Examination are then eligible to appear for the Main Examination, which consists of nine papers, including an Essay, General Studies I to IV, Optional Papers I and II, and Language Papers.
The CSAT exam is a highly competitive exam, and lakhs of candidates appear for it every year to pursue a career in the Indian Civil Services. The Indian Civil Services is considered to be one of the most prestigious and sought-after careers in India, and clearing the CSAT exam is a crucial step in the selection process.
Special recruitment areas
Accounting and Auditing
Accounting and auditing are two closely related fields that are essential for the financial management and reporting of any organization.
Accounting refers to the process of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions to provide accurate and reliable financial information for decision-making purposes. The main objective of accounting is to provide information about the financial position, performance, and cash flows of an organization. Accounting includes various activities such as bookkeeping, financial statement preparation, budgeting, and analysis.
Auditing, on the other hand, is the process of evaluating and verifying financial records and statements to ensure their accuracy, completeness, and compliance with the relevant laws and regulations. Auditing can be internal or external. Internal auditing is performed by employees within an organization, while external auditing is performed by independent auditors.
Auditing is essential for ensuring the reliability of financial information and helps to identify and prevent financial fraud and errors. Auditing includes activities such as risk assessment, audit planning, conducting audit procedures, and preparing audit reports.
Both accounting and auditing are critical for the financial management and reporting of any organization, and professionals in these fields play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial information.
Tax Advisory Service
Tax advisory services are professional services provided by tax experts to individuals and businesses to help them navigate complex tax laws and regulations and optimize their tax strategies.
Tax advisory services can include a wide range of services, such as tax planning, compliance, and consulting. Tax advisors work closely with their clients to understand their financial situation and develop tax strategies that can help minimize tax liability and maximize tax savings.
Some of the common tax advisory services include:
- Tax planning and strategy development: Tax advisors help clients develop effective tax strategies that are aligned with their financial goals and objectives.
- Tax compliance: Tax advisors ensure that clients comply with tax laws and regulations and file tax returns accurately and timely.
- Tax consulting: Tax advisors provide advice and guidance on a range of tax-related issues, such as tax disputes, tax credits, tax incentives, and tax implications of business transactions.
- International tax advisory services: Tax advisors help multinational businesses navigate the complexities of international tax laws and regulations and optimize their cross-border tax strategies.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Tax advisors provide tax due diligence, structuring advice, and post-transaction integration support for mergers and acquisitions.
Tax advisory services can help individuals and businesses save money, reduce their tax liabilities, and manage risks associated with tax compliance.
Financial service
Financial services refer to the services provided by financial institutions to individuals, businesses, and governments to help them manage their money and achieve their financial goals. Financial services include a wide range of services, such as banking, investment management, insurance, and financial planning.
Some of the common financial services include:
- Banking services: This includes services such as opening bank accounts, issuing debit and credit cards, and providing loans and mortgages.
- Investment management: This includes services such as managing investment portfolios, providing investment advice, and offering wealth management services.
- Insurance services: This includes services such as providing life insurance, health insurance, property insurance, and other types of insurance.
- Financial planning: This includes services such as retirement planning, tax planning, and estate planning.
- Trading services: This includes services such as online trading, stock trading, and foreign exchange trading.
- Payment services: This includes services such as mobile payments, electronic fund transfers, and online payment systems.
- Advisory services: This includes services such as financial analysis, risk management, and corporate finance advisory.
Financial services are critical for the functioning of the economy and play a vital role in facilitating transactions, managing risks, and providing financial security to individuals and businesses.
Commercial banking
Anyone can enroll themself in commercial banking as an employee.
Commercial banking is a type of banking service that is primarily focused on providing financial services to businesses, corporations, and other institutions. The main function of commercial banks is to accept deposits from customers and use those deposits to make loans and provide other financial services.
Commercial banks offer a wide range of services to their customers, including:
- Deposits: Commercial banks accept various types of deposits, such as checking accounts, savings accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- Loans: Commercial banks make loans to businesses and corporations for a variety of purposes, such as working capital, capital expenditures, and real estate financing.
- Trade finance: Commercial banks provide trade finance services, such as letters of credit, to facilitate international trade.
- Cash management: Commercial banks offer cash management services to help businesses manage their cash flows and liquidity.
- Credit cards: Commercial banks issue credit cards to businesses and consumers.
- Foreign exchange: Commercial banks provide foreign exchange services to businesses and individuals who need to exchange currencies.
- Investment services: Commercial banks offer investment services, such as mutual funds and managed accounts, to help businesses and individuals grow their wealth.
Commercial banks play a vital role in the economy by providing businesses with the financing they need to operate and grow. They also play a critical role in facilitating transactions and managing risks in the financial system.
International banking
International banking refers to banking services that are provided across national borders. An international banking job typically involves working for a financial institution that provides banking services to clients in different countries. The job may involve working in different areas, such as international trade finance, foreign exchange, cross-border lending, and investment banking.
Some common roles in international banking include:
- Relationship manager: A relationship manager in international banking is responsible for managing relationships with clients in different countries. The job involves understanding the needs of clients and providing them with customized solutions.
- Trade finance specialist: A trade finance specialist in international banking is responsible for facilitating international trade transactions, such as issuing letters of credit, providing financing, and managing risk.
- Foreign exchange trader: A foreign exchange trader in international banking is responsible for buying and selling currencies to facilitate international transactions.
- Cross-border lender: A cross-border lender in international banking is responsible for providing financing to clients in different countries.
- Investment banker: An investment banker in international banking is responsible for providing advice on mergers and acquisitions, debt and equity offerings, and other types of financial transactions.
- Risk manager: A risk manager in international banking is responsible for managing the risks associated with international banking activities, such as credit risk, market risk, and operational risk.
International banking jobs require a strong understanding of global markets, financial products, and regulatory requirements. They also require excellent communication and interpersonal skills to work effectively with clients from different cultures and backgrounds.
Insurance service
An insurance service job involves providing a range of services related to insurance products. Insurance is a financial product that provides protection against various risks, such as loss or damage to property, illness or injury, and death. Insurance companies offer a variety of products, such as life insurance, health insurance, property and casualty insurance, and liability insurance.
Some common roles in the insurance industry include:
- Insurance agent or broker: An insurance agent or broker sells insurance products to individuals and businesses. They help clients understand their insurance needs, recommend appropriate policies, and assist with claims.
- Underwriter: An underwriter is responsible for assessing risk and determining the terms and conditions of insurance policies. They review applications, analyze data, and decide whether to offer coverage and at what price.
- Claims adjuster: A claims adjuster investigates insurance claims and determines the amount of compensation that should be paid to policyholders. They review policy terms, assess damages, and negotiate settlements.
- Actuary: An actuary uses statistical and mathematical models to assess risk and develop insurance policies. They analyze data, estimate future losses, and design policies that balance risk and affordability.
- Risk manager: A risk manager is responsible for identifying and mitigating risks for individuals and businesses. They develop risk management strategies, assess potential losses, and recommend insurance coverage to protect against those losses.
Insurance service jobs require a strong understanding of insurance products, regulatory requirements, and risk management principles. They also require excellent communication, analytical, and problem-solving skills to work effectively with clients, underwriters, and other professionals in the insurance industry.
Telecommunication service and BPO’s
Telecommunication and BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) services are two related industries that involve providing services to businesses and consumers through communication technologies.
Telecommunication services refer to the transmission of information over long distances using communication technologies such as telephones, the internet, and wireless devices. Telecommunication companies provide services such as voice and data communications, internet connectivity, and video conferencing. They also provide equipment and devices such as mobile phones, routers, and modems.
BPO services refer to the outsourcing of specific business processes, such as customer service, accounting, human resources, and back-office operations, to third-party service providers. BPO companies provide services such as customer support, technical support, data entry, and other business process services.
The telecommunication and BPO industries are closely related because many BPO services are delivered through telecommunication technologies. For example, customer service representatives may work remotely and communicate with customers through phone, email, or chat.
Common roles in the telecommunication and BPO industries include:
- Customer service representative: A customer service representative is responsible for assisting customers with their inquiries, complaints, and other issues. They may communicate with customers through phone, email, or chat.
- Technical support specialist: A technical support specialist provides assistance to customers with technical issues related to products and services. They may troubleshoot software, hardware, and connectivity issues.
- Sales representative: A sales representative is responsible for selling products and services to customers. They may work in telesales, making calls to customers to promote products and services.
- Data entry specialist: A data entry specialist is responsible for inputting data into computer systems, databases, or spreadsheets. They may also be responsible for verifying data accuracy and completeness.
- Back-office support staff: Back-office support staff provides administrative and support services for the business, such as finance, accounting, and human resources.
Telecommunication and BPO jobs require strong communication skills, technical knowledge, and customer service skills. They also require excellent time management, organizational, and problem-solving skills to work effectively in fast-paced environments.
Manufacturing services
Manufacturing service refers to the process of creating or producing goods or products using raw materials and equipment. The manufacturing industry is involved in the production of a wide range of products, including consumer goods, machinery, equipment, chemicals, and industrial materials.
The manufacturing process typically involves several stages, including designing the product, sourcing raw materials, production, quality control, packaging, and distribution. Manufacturing companies also often employ skilled workers who operate machinery and equipment to produce the final product.
There are many different types of manufacturing services, including:
- Custom manufacturing: Custom manufacturing involves creating unique products according to the specific needs and requirements of individual customers.
- Contract manufacturing: Contract manufacturing involves producing products on behalf of other companies. The manufacturing company provides the equipment, labor, and materials needed to produce the product.
- Batch production: Batch production involves producing a specific quantity of a product at one time. This process is often used for products with limited demand.
- Continuous production: Continuous production involves the continuous production of goods, typically using an assembly line or other automated manufacturing processes.
- Just-in-time manufacturing: Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing involves producing goods based on the specific needs and demands of customers, with minimal inventory or storage of finished products.
Common roles in the manufacturing industry include:
- Production manager: A production manager oversees the manufacturing process, ensuring that production targets are met and that quality standards are maintained.
- Production line worker: A production line worker operates machinery and equipment on the production line to produce goods or products.
- Quality control inspector: A quality control inspector checks finished products to ensure they meet quality standards and specifications.
- Industrial engineer: An industrial engineer is responsible for designing and improving manufacturing processes, equipment, and systems.
- Supply chain manager: A supply chain manager oversees the logistics and supply chain of the manufacturing process, including sourcing materials and distributing finished products.
Manufacturing jobs require strong technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work well in a team.
Government Service
Government service refers to the employment opportunities available in various government organizations at the local, state, or federal level. These jobs are typically associated with providing public services and serving the needs of the community or society as a whole.
Government services encompass a broad range of industries and sectors, including education, healthcare, transportation, law enforcement, defense, social services, and many others. Some common examples of government service jobs include:
- Civil service: Civil service jobs refer to positions within government agencies that require a competitive examination and have specific job requirements. Examples of civil service jobs include clerks, administrative assistants, and law enforcement officers.
- Education: Government service jobs in education include teachers, school administrators, and educational support staff at the local, state, and federal levels.
- Healthcare: Government service jobs in healthcare include doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals who work in government-run hospitals, clinics, and healthcare centers.
- Law enforcement: Government service jobs in law enforcement include police officers, FBI agents, and other law enforcement officials who work to ensure public safety and uphold the law.
- Social services: Government service jobs in social services include social workers, child welfare workers, and other professionals who provide assistance to vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and people with disabilities.
Working in government service often requires specific qualifications, such as a degree or specialized training, as well as an understanding of government policies and regulations. These jobs can offer competitive salaries, job security, and opportunities for career advancement.
Policy Planning
Policy planning job refers to the process of developing and implementing policies and strategies that guide decision-making and actions within an organization, government, or society. Policy planning involves identifying problems, assessing potential solutions, and making recommendations to help achieve specific goals and objectives.
Policy planners typically work for government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector organizations to develop policies and strategies that address a wide range of social, economic, and environmental issues. Some common examples of policy planning jobs include:
- Government policy analyst: A policy analyst works within a government agency to analyze policy proposals, evaluate their potential impact, and make recommendations for improving them.
- Non-profit program coordinator: A program coordinator works within a non-profit organization to develop and implement programs that address specific social issues such as poverty, health care, or education.
- Private sector strategic planner: A strategic planner works within a private sector organization to develop and implement strategies that support the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Environmental planner: An environmental planner works within a government agency or private sector organization to develop policies and strategies that promote environmental sustainability.
Policy planners typically require strong analytical skills, excellent communication skills, and the ability to work effectively with stakeholders from diverse backgrounds. They may also need to have specialized knowledge in a particular field, such as economics, environmental science, or public health.
Educational Institute
A private coaching job refers to the profession of providing personalized education and training services to individuals or small groups. Private coaches may work independently or as part of a coaching or tutoring agency, and may specialize in a wide range of subjects and skills.
Private coaching jobs can be found in a variety of fields, including academics, sports, music, art, and personal development. Some common examples of private coaching jobs include:
- Academic tutor: An academic tutor provides one-on-one or small group instruction in academic subjects such as math, science, or language arts.
- Sports coach: A sports coach provides individual or team coaching in a particular sport, helping athletes to develop their skills, techniques, and strategies.
- Music teacher: A music teacher provides private instruction in a particular musical instrument or genre, helping students to improve their playing skills and develop their musical abilities.
- Art instructor: An art instructor provides private instruction in drawing, painting, sculpture, or other artistic techniques, helping students to develop their artistic abilities and creative expression.
Private coaching jobs typically require specialized knowledge and skills in a particular subject or field, as well as the ability to communicate effectively and motivate students. They may work with students of all ages and skill levels, from elementary school students to adult learners, and may provide coaching services in person or online.
IT (Information and technology)
Information technology (IT) jobs refer to the professions related to the development, installation, and maintenance of computer software, hardware, and networks. IT jobs can be found in a variety of industries, including finance, healthcare, education, government, and entertainment. Some common examples of IT jobs include:
- Software developer: A software developer designs and develops computer programs and applications for a variety of industries, including finance, healthcare, and e-commerce.
- Network administrator: A network administrator is responsible for the installation, maintenance, and security of computer networks, including local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
- Cybersecurity analyst: A cybersecurity analyst helps to protect computer systems and networks from cyberattacks by identifying and preventing security breaches.
- Database administrator: A database administrator is responsible for the installation, maintenance, and security of databases used by an organization.
- Technical support specialist: A technical support specialist provides assistance to users of computer hardware and software, troubleshooting problems and providing guidance on how to use various software applications.
IT jobs typically require specialized knowledge and skills in computer science, programming, networking, and cybersecurity. They may also require strong communication and problem-solving skills, as well as the ability to work effectively in a team. IT jobs are in high demand due to the increasing reliance on technology in all aspects of business and daily life.
Special Job titles for B.com graduate
Chartered Accountant (CA)
A Chartered Accountant (CA) is a professional accountant who has completed the required training and education to earn the CA designation. CAs are trained in a wide range of financial and business skills, including accounting, auditing, taxation, and financial management. They play a crucial role in helping individuals and organizations manage their finances and make informed financial decisions.
To become a CA, one must complete a series of rigorous exams and meet the educational and professional requirements set by a professional accounting body, such as the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (ICAEW) or the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI). These requirements typically include a combination of education, practical experience, and exams, and can take several years to complete.
Once qualified, CAs may work in a variety of settings, including accounting firms, consulting firms, government agencies, and corporations. They may provide a range of services, including financial reporting, auditing, taxation, and financial consulting. CAs are held to high ethical and professional standards and are expected to maintain ongoing education and training to stay up to date with changes in accounting standards and practices.
Marketing management job
Marketing management is a career path that involves overseeing the marketing strategies and activities of a business or organization. The primary goal of marketing management is to promote a product, service, or brand to the target market and increase sales and revenue.
As a marketing manager, your responsibilities may include:
- Developing and executing marketing plans: You will need to develop and implement marketing strategies and plans that align with the overall business objectives. This includes conducting market research, identifying target audiences, creating campaigns, and monitoring their effectiveness.
- Managing budgets: You will be responsible for managing the marketing budget and ensuring that campaigns are delivered within budget constraints.
- Supervising and mentoring marketing teams: You will be responsible for supervising and managing a team of marketing professionals, including copywriters, designers, and digital marketers. This includes setting objectives, monitoring performance, and providing feedback and coaching.
- Analyzing market trends and competitors: You will need to stay up to date with market trends, industry developments, and competitor activities to identify opportunities and threats for the business.
- Measuring and reporting on marketing performance: You will need to analyze marketing metrics such as sales revenue, customer engagement, and return on investment (ROI) and report on the effectiveness of marketing campaigns to senior management.
Overall, marketing management is a dynamic and exciting field that requires creativity, strategic thinking, and excellent communication skills. A successful marketing manager needs to be able to identify market opportunities, develop effective marketing strategies, and manage a team to execute those strategies successfully.
Investment Banker
An investment banker is a professional who works with businesses and other organizations to help them raise capital, buy or sell assets, and provide strategic financial advice. Investment bankers typically work for investment banks, which are financial institutions that provide a range of services related to securities trading, underwriting, and investment management.
Here are some of the key responsibilities of an investment banker:
- Raising capital: Investment bankers help businesses raise capital through the issuance of stocks, bonds, or other securities. This involves creating financial models, analyzing market conditions, and developing strategies to attract investors.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Investment bankers advise clients on mergers, acquisitions, and other corporate transactions. This includes conducting due diligence, developing valuation models, and negotiating the terms of the deal.
- Strategic financial advice: Investment bankers provide strategic financial advice to clients, including recommendations on capital structure, risk management, and financial performance.
- Securities trading: Investment bankers may engage in securities trading, including buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other securities on behalf of clients.
- Business development: Investment bankers are responsible for developing new business opportunities and building relationships with clients and other stakeholders in the financial industry.
To become an investment banker, you typically need a strong background in finance, economics, or a related field. Most investment bankers hold a master’s degree in business administration (MBA) or a related field, and many also hold professional certifications such as the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation.
Entry-level positions typically require previous experience in finance, often through internships or entry-level jobs at investment banks. Successful investment bankers are typically strong analytical thinkers, excellent communicators, and skilled negotiators with a deep understanding of the financial industry and the markets in which they operate.
Human resource manager (HR)
A Human Resource (HR) Manager is responsible for overseeing all aspects of a company’s human resources policies and procedures. They play a critical role in ensuring that the organization’s employees are managed efficiently, effectively, and in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Some of the key responsibilities of an HR Manager include:
- Recruitment and Staffing: HR Managers are responsible for attracting, recruiting, and retaining top talent for the organization. This includes identifying hiring needs, sourcing candidates, conducting interviews, and managing the onboarding process.
- Employee Relations: HR Managers are responsible for managing employee relations and addressing employee concerns and issues. They may mediate conflicts, investigate complaints, and take corrective actions as needed.
- Benefits and Compensation: HR Managers are responsible for managing employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. They also ensure that the organization’s compensation policies are competitive and aligned with industry standards.
- Training and Development: HR Managers are responsible for developing and implementing employee training and development programs. They work with managers and employees to identify training needs, design training programs, and monitor progress and effectiveness.
- Compliance: HR Managers are responsible for ensuring that the organization is compliant with all applicable laws and regulations related to employment. This includes managing employee files, ensuring compliance with labor laws, and keeping up-to-date with changes in employment laws and regulations.
Overall, the HR Manager plays a vital role in ensuring that the organization has the right people, in the right positions, with the right training, and compensation to achieve its goals. Successful HR Managers possess strong communication and interpersonal skills, an understanding of employment laws and regulations, and the ability to build relationships with employees at all levels of the organization.
Business accountant and taxation
A business accountant and taxation professional is responsible for managing a company’s financial records, ensuring that taxes are filed accurately and on time, and providing financial advice to company management.
Some of the key responsibilities of a business accountant and taxation professional include:
- Bookkeeping: The professional is responsible for maintaining the financial records of the company, including keeping track of income, expenses, and profits.
- Financial Reporting: The professional is responsible for preparing financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These statements are used to inform management and stakeholders of the company’s financial performance.
- Tax Planning: The professional is responsible for advising the company on tax planning strategies, such as deductions and credits, to minimize the amount of taxes owed.
- Tax Compliance: The professional is responsible for ensuring that the company complies with tax laws and regulations. This includes preparing and filing tax returns, as well as responding to tax audits and inquiries.
- Financial Analysis: The professional is responsible for analyzing the company’s financial data to identify trends and patterns. This information is used to make strategic decisions and inform management of the company’s financial performance.
- Advisory Services: The professional is responsible for providing financial advice to company management, such as recommending ways to improve profitability or reduce expenses.
Successful business accountants and tax professionals have a strong understanding of financial accounting principles and tax laws and regulations. They possess excellent analytical and problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to communicate financial information to non-financial stakeholders.
Additionally, they must stay up-to-date with changes in tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and optimize the company’s financial performance.
Retail Manager
A retail manager is responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations of a retail store or chain of stores. They are responsible for managing employees, ensuring customer satisfaction, and driving sales and profits.
Some of the key responsibilities of a retail manager include:
- Staff Management: The manager is responsible for recruiting, training, and supervising staff members. They ensure that employees are knowledgeable about the products they sell and that they provide excellent customer service.
- Inventory Management: The manager is responsible for managing the inventory of the store, including ordering products, monitoring stock levels, and ensuring that the store has adequate supplies.
- Sales Management: The manager is responsible for setting sales goals, monitoring sales performance, and implementing strategies to increase sales and profits.
- Customer Service: The manager is responsible for ensuring that customers have a positive shopping experience. They may resolve customer complaints, handle returns, and oversee customer service operations.
- Marketing and Merchandising: The manager is responsible for creating and implementing marketing and merchandising strategies to attract customers and increase sales. This may involve creating promotional campaigns, managing displays and signage, and monitoring competitor pricing and promotions.
- Financial Management: The manager is responsible for managing the financial aspects of the store, including budgeting, forecasting, and managing expenses.
Successful retail managers possess excellent communication and leadership skills, a deep understanding of the retail industry, and the ability to analyze data and make strategic decisions. They are also skilled at managing and motivating employees, resolving conflicts, and maintaining a positive and productive work environment.
Company Secretary
A Company Secretary is a senior-level executive who is responsible for ensuring that a company complies with legal and regulatory requirements. They act as a link between the company’s board of directors, senior management, and various external stakeholders such as regulators, shareholders, and auditors.
Some of the key responsibilities of a Company Secretary include:
- Corporate Governance: The Company Secretary is responsible for ensuring that the company complies with legal and regulatory requirements related to corporate governance. This includes ensuring that the company adheres to the requirements of the Companies Act, maintains accurate records, and files required documentation.
- Board and Shareholder Meetings: The Company Secretary is responsible for organizing and attending board and shareholder meetings. They prepare agendas, take minutes, and ensure that decisions are properly recorded and communicated.
- Compliance: The Company Secretary is responsible for ensuring that the company complies with all applicable laws and regulations. This includes monitoring changes to laws and regulations and ensuring that the company implements any necessary changes.
- Risk Management: The Company Secretary is responsible for overseeing the company’s risk management processes. This includes identifying potential risks and implementing processes to mitigate them.
- Shareholder Relations: The Company Secretary is responsible for managing relationships with the company’s shareholders. This includes communicating with shareholders, responding to their queries, and ensuring that their rights are protected.
- Corporate Strategy: The Company Secretary plays a key role in developing and implementing the company’s corporate strategy. They work closely with the board of directors and senior management to develop long-term plans and ensure that the company’s activities align with its strategic objectives.
Successful Company Secretaries possess excellent communication and interpersonal skills, strong analytical and problem-solving abilities, and a deep understanding of legal and regulatory requirements. They are also highly organized and detail-oriented, with the ability to manage multiple tasks and priorities effectively.
Is a B.com degree worth it?
Yes, a B.Com (Bachelor of Commerce) degree can be worth it for many individuals, depending on their career goals and aspirations.
A B.Com degree provides a strong foundation in business and commerce-related subjects such as accounting, economics, finance, and management. This can be helpful for individuals seeking careers in fields such as accounting, banking, finance, or business administration. Additionally, a B.Com degree can also be beneficial for individuals interested in pursuing higher education such as an MBA or a Master’s degree in a related field.
Some potential benefits of earning a B.Com degree include:
- Enhanced career prospects: A B.Com degree can prepare individuals for a variety of entry-level roles in accounting, finance, marketing, and other business-related fields.
- Transferable skills: The skills and knowledge gained through a B.Com degree such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and analytical skills are transferable and can be applied in a variety of industries and job roles.
- Higher earning potential: A B.Com degree can potentially lead to higher salaries and better career advancement opportunities, especially when coupled with relevant work experience and professional certifications.
However, it is important to note that the value of a B.Com degree may vary depending on factors such as the reputation of the college or university, the quality of the program, and the individual’s performance and experience. It is important to research and carefully consider your career goals and options before making a decision to pursue a B.Com degree.
Can I get a Job with a B.com degree?
Yes, you can definitely get a job after completing a B.Com (Bachelor of Commerce) degree. A B.Com degree provides a strong foundation in business and commerce-related subjects, which can be helpful for individuals seeking entry-level roles in various industries.
Some common job roles that B.Com graduates may consider include:
- Accountant: B.Com graduates can work as accountants in various organizations, including accounting firms, corporations, and government agencies.
- Financial analyst: B.Com graduates can also work as financial analysts, helping organizations make informed financial decisions.
- Tax consultant: B.Com graduates can work as tax consultants and help individuals and organizations with tax planning and compliance.
- Business development executive: B.Com graduates can work in business development roles, helping companies identify new business opportunities and build partnerships.
- Marketing executive: B.Com graduates can also work in marketing roles, helping companies promote their products and services to customers.
There are many other job roles that B.Com graduates can consider, depending on their skills and interests. It’s important to note that while a B.Com degree can be helpful in securing entry-level roles, it may also be important to gain relevant work experience and professional certifications to advance in your career.
Can I become a software engineer with a B.com degree?
While a B.Com (Bachelor of Commerce) degree does not provide the technical skills and knowledge necessary to become a software engineer, it is possible to transition into a career in software engineering with additional education and training.
To become a software engineer, you typically need to have a degree in computer science, software engineering, or a related field. However, if you have a B.Com degree and are interested in pursuing a career in software engineering, there are some steps you can take to make the transition:
- Consider pursuing additional education: One option is to consider pursuing a master’s degree in computer science or software engineering. This can provide you with the technical skills and knowledge needed to become a software engineer.
- Learn programming languages and software development skills: You can start learning programming languages such as Java, Python, or C++ and software development skills through online courses, coding boot camps, or self-study.
- Build a portfolio of projects: You can work on personal coding projects or contribute to open-source projects to build your skills and create a portfolio that demonstrates your abilities to potential employers.
- Gain relevant work experience: Consider taking on internships or entry-level roles in software development to gain experience and build your skills.
While the transition from a B.Com degree to a software engineering career may take some time and effort, it is possible with dedication and commitment to learning the necessary skills.
List of top B.com colleges
- Shri Ram College of Commerce, Delhi University
- Lady Shri Ram College for Women, Delhi University
- Loyola College, Chennai
- Christ University, Bangalore
- Hindu College, Delhi University
- St. Xavier’s College, Mumbai
- Hansraj College, Delhi University
- St. Joseph’s College, Bangalore
- Narsee Monjee College of Commerce and Economics, Mumbai
- Madras Christian College, Chennai
Top M.com colleges in India
- Delhi School of Economics, Delhi University
- Loyola College, Chennai
- Christ University, Bangalore
- Madras School of Economics, Chennai
- Shri Ram College of Commerce, Delhi University
- St. Joseph’s College, Bangalore
- Hindu College, Delhi University
- St. Xavier’s College, Mumbai
- Narsee Monjee College of Commerce and Economics, Mumbai
- Presidency College, Chennai
Top MBA colleges in India
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Bangalore
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Calcutta
- XLRI Xavier School of Management, Jamshedpur
- Indian School of Business (ISB), Hyderabad
- Faculty of Management Studies (FMS), Delhi University
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Lucknow
- S. P. Jain Institute of Management and Research, Mumbai
- Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Kozhikode
- Jamnalal Bajaj Institute of Management Studies, Mumbai
Top MCA colleges in India
- National Institute of Technology (NIT), Trichy
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani
- Department of Computer Science, University of Pune
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore
- Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore
- Christ University, Bangalore
- Institute of Management Studies (IMS), Ghaziabad
- Department of Computer Applications, NIT Kurukshetra
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai
- Department of Computer Science, University of Hyderabad
Top Law (LLB) colleges in India
- National Law School of India University (NLSIU), Bangalore
- National Academy of Legal Studies and Research (NALSAR) University of Law, Hyderabad
- Faculty of Law, Delhi University
- National Law University, Jodhpur
- WB National University of Juridical Sciences, Kolkata
- Symbiosis Law School, Pune
- Government Law College, Mumbai
- National Law University, Delhi
- Jindal Global Law School, Sonipat
- Gujarat National Law University, Gandhinagar
Also Read– Psychology lessons to become a successful
FAQ’s
-
What to do after B.com?

Since B.com opens up a wide field of opportunities for students. One can go with any of the below courses, degrees, certificates, and jobs:
Degree courses–
MBA
PGDM
M.com
MCA
LLB
B.EdProfessional certificate courses–
CA
CS
ACCA
CMA
CFA
CFPSkill development courses–
Data Science
Business Analytics
Stock market
programming
Web design/ App development
VFX and Animation
Digital Marketing
Ethical Hacking
Personality development coursesGovernment jobs–
SSC CGL
IBPS PO
RRB
CSATspecial recruitment areas–
Accounting and Auditing
Tax advisory service
Financial service
commercial banking
International banking
Insurance service
Telecommunication service and BPO’s
Manufacturing service
Government service
Policy Planning
Educational Institute
Informational technologySpecial job titles for B.com graduates–
Chartered Accountant (CA)
Marketing Management
Investment Banker
Human resource manager
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
Chartered Public Accountant (CPA)
Actuary
Cost accountant
Business Accountant and taxation
Retail manager
Company Secretary
Personal Financial Advisor
Research Analyst
Chief Executive Officer (CFO)
Entrepreneur -
What are the famous courses after B.com?
M.com
MCA
MBA
LLB -
What Jobs are available after B.com?
SSC CGL
IBPS PO
RRB
Programming
Web development
App Development
Accountant
Manager
Private tutor

